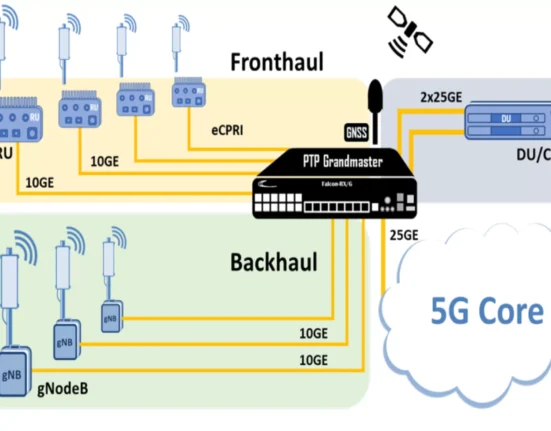
With industries continuing to look for innovative ways to improve their operational capabilities, the fusion of 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT) is openly discussed. IoT has already been a game changer for various sectors and the businesses that represent them. However, introducing 5G’s high-speed and low latency promises to add even more value to IoT.
Still, much like with every new technological leap, moving forward isn’t always as easy as it sounds. As organizations begin looking at the potential applications of 5G and IoT, a variety of challenges still need to be addressed to start seeing sustainable use cases and benefits.
What Exactly is 5G Technology and What Does it Do?
You may have heard of 3G or 4G technology when referring to cellular data-transfer technology. 5G is the latest version of this technology. However, its improvements to previous versions aren’t just concentrated on faster download rates. It also is a significant leap forward in how mobile devices can communicate with one another, allowing for improved speeds of up to 10 gigabits per second.
The real value of 5G technology comes from its ability to significantly reduce the latency of data transfers when traveling from one source to another. This translates to an ultra-low latency level of just milliseconds, making connected devices much more reliable and is an important feature when used in IoT applications.
Some of the applications this new technology can support are self-driving cars capable of reacting through split-second data analysis, smart cities running on interconnect IoT sensors, and even real-time remote surgery or diagnosis applications in hospitals and other healthcare facilities.
How is 5G Positioned to Improve IoT Technology?
5G isn’t just a simple upgrade from previous cellular technologies. This next-generation technology improves on various elements, including:
Lower Latency and Better Speed
5G technology can move at lightning-fast speeds and provide instantaneous data transfers to and from IoT devices. The potential use cases for this technology are still being realized, but there are countless scenarios in which this can be useful.
For example, factor sensors in manufacturing plants can detect potential equipment malfunctions as soon as they happen automatically, allowing for the adjustment of settings to prevent large-scale breakdowns.
Improved Network Capabilities
The limitations of previous IoT versions often came from network restrictions that could cause intermittent connectivity issues. This would make it challenging to scale IoT solutions past a certain point.
With the introduction of 5G technology, these barriers are quickly being taken down, allowing for much more scalable IoT solutions. This added flexibility has become critical for introducing more complex applications, including smart city infrastructure, to optimize energy use.
Increased Usability
The introduction of 5G technology in mobile devices and sensors has unlocked various new possibilities for increased industry use cases. A notable example of this is in the automotive industry and in the ongoing development of autonomous vehicles.
With most modern vehicles now using more GPS and AI capabilities, 5G technology helps to support the necessary foundation required to support the complex infrastructure needed to ensure their seamless operation.
Where Are We Currently When It Comes to 5G and IoT Integrations?
Although 5G technology is no longer new, it still needs to be widely adopted due to its various infrastructural limitations. Even though certain regions, like the U.S., have more widespread adoption and support for 5G technology, global saturation of the technology will still take some time.
Telecommunication companies have heavily invested in the development of 5G infrastructure. However, due to the increased costs and complexities of ensuring widespread adoption, it may take years for 5 G to reach the level of 4G.
That being said, 5G technology is rapidly gaining more traction in IoT spaces. Manufacturing industries are currently beginning to use 5G technology in their IoT sensors to create “smart factories” that rely on data collection and transmission devices to optimize production runs and help ensure quality control measures.
With 5G technology continuing to mature, the integration capabilities in IoT devices are promising to revolutionize unprecedented levels of diverse sectors like healthcare and public and private transportation.
Despite the potential of 5G and IoT integrations, there are still a variety of challenges that also need to be actively addressed:
- Infrastructure Challenges – The financial requirements of 5G deployments, especially in certain regions that still require substantial upgrades in existing cellular towers and supporting systems, could continue to slow-down the adoption of the newer technology.
- Incompatibility with Legacy Devices – Older IoT devices often lack the compatibility to support seamless 4G/5G transitions. This can create a variety of obstacles for organizations needing to modernize and scale their IoT infrastructure.
- Potential Security Issues – The increased connectivity and data exchanges when introducing 5G with IoT can raise significant security and privacy concerns. As the technology continues to mature, organizations need to develop a deeper understanding of the modern threat landscape to continuously make 5G technologies more secure
- Energy Consumption – The increasing data transmission demands of 5G technology can rapidly deplete power sources of IoT devices, which can pose significant issues for challenges that rely on continuous uptime and where frequent battery replacements can be impractical.
How is the Future of IoT Looking?
Projections suggest that 25 billion IoT devices will be up and running around the world by 2025 and are only expected to expand even further as more businesses rely on the technology.
The growth of edge computing and AI-driven technologies coupled with 5G is also improving the potential of IoT and providing seamless communication capabilities coupled with powerful real-time analytics capabilities.
However, these exciting new developments don’t absolve organizations from needing to make important ethical considers when integrating this new technology. The responsible adoption of IoT requires due diligence in order to capitalize on the improved capabilities of 5G without compromising network integrity or customer privacy.
Author Bio:
Subbu Seetharaman is the Director Of Engineering, at Lantronix, a global provider of turnkey solutions and engineering services for the internet of things (IoT). Subbu is an engineering executive with over 25 years experience in leading software development teams, building geographically distributed, high performing teams involved in developing complex software products around programmable hardware devices.